本文为廖雪峰老师的手写Spring笔记中的MVC一节,仅作个人学习使用。
在本节实现Summer中的MVC,我们主要涉及到DispatcherServlet,Controller,RestController,ViewResolver组件,关注于MVC中的核心功能。
启动IOC
首先我们需要明确一些关于tomcat,servlet,IOC之间的关系,更多的是包含关系:启动IoC容器。
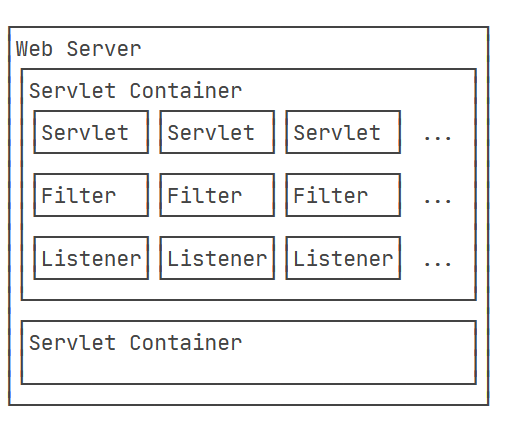
上图是传统Java web的架构图,一个Tomcat服务器可以运行多个web项目,也就是Servlet Container。每个Container中都含有三大组件:servlet,Filter,Listener。
而在Spring MVC中,引入了IOC容器,并且简化了操作流程,具体变为了下图:
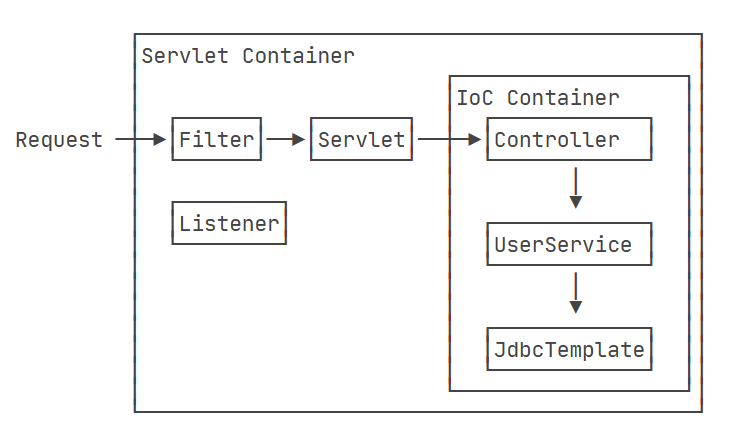
上图的Servlet实际上就是DispatcherServlet,我们把所有的请求都交给DispatcherServlet处理,它包含着IOC的引用,我们通过IOC获取到具体的操作逻辑。
以Tomcat为例,下面是整个服务启动的流程:
- 启动服务器,即执行Tomcat的
main()方法; - Tomcat根据配置或自动检测到一个
xyz.war包后,为这个xyz.war应用程序创建Servlet容器; - Tomcat继续查找
xyz.war定义的Servlet、Filter和Listener组件,按顺序实例化每个组件(Listener最先被实例化,然后是Filter,最后是Servlet); - 用户发送HTTP请求,Tomcat收到请求后,转发给Servlet容器,容器根据应用程序定义的映射,把请求发送个若干Filter和一个Servlet处理;
- 处理期间产生的事件则由Servlet容器自动调用Listener。
在第三点中,由于我们只有一个DispatcherServlet,所以可以采用ServletContextListener#contextInitialized方法,监听Servlet Container的初始化,在这时去创建IOC(扫描获取Controller Bean),创建DispatcherServlet并注册到Tomcat中。
创建Listener类:
- 调用PropertyResolver配置项,我们将配置项放置到
/application.yml下,设置编码。 - 初始化IOC,其中configuration是在web.xml中配置的,对应的是配置类的包路径。
- 注册DispatcherServlet。
- 将IOC的引用挂载到ServletContext上。
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
var servletContext = sce.getServletContext();
var propertyResolver = WebUtils.createPropertyResolver();
String encoding = propertyResolver.getProperty("${summer.web.character-encoding:UTF-8}");
servletContext.setRequestCharacterEncoding(encoding);
servletContext.setResponseCharacterEncoding(encoding);
var applicationContext = createApplicationContext(servletContext.getInitParameter("configuration"), propertyResolver);
// register DispatcherServlet:
WebUtils.registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext, propertyResolver);
servletContext.setAttribute("applicationContext", applicationContext);
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
if (sce.getServletContext().getAttribute("applicationContext") instanceof ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.close();
}
}
ApplicationContext createApplicationContext(String configClassName, PropertyResolver propertyResolver) {
if (configClassName == null || configClassName.isEmpty()) {
throw new NestedRuntimeException();
}
Class<?> configClass;
try {
configClass = Class.forName(configClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new NestedRuntimeException();
}
return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(configClass, propertyResolver);
}
}
目前DispatchServlet逻辑还比较简单,是由单纯的初始化,现在访问所有的路径的会返回Hello,world。
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public DispatcherServlet(ApplicationContext applicationContext, PropertyResolver properyResolver) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
this.applicationContext.close();
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
logger.info("{} {}", req.getMethod(), req.getRequestURI());
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
pw.write("<h1>Hello, world!</h1>");
pw.flush();
}
}
MVC
在Summer中,对于控制器提供@Controller,@RestController注解。
对于Dispatcher,提供@GetMapping,@PostMapping,@ResponseBody注解。
对于参数,提供@PathVariable,@RequestParam,@RequestBody,@ServletVariable。
具体的作用和spring mvc大致相同,不再赘述。有一些不同会在下方说明。
可以考虑一下Spring MVC中,我们是怎么定义一个接口方法的,可能是下面的样子:
@RestController
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return name;
}
}
可以抽象出来三个很重要的类型:Class,Method,Param。
首先只有表示了@Controller或@RestController的类才可以看作一个控制器。
我们对其中包含@GetMapping和@PostMapping的方法称作一个处理特定URL的处理器(dispatcher)。
dispatcher的参数抽象为Param。
定义如下:
class Dispatcher {
final static Result NOT_PROCESSED = new Result(false, null);
boolean isRest;
boolean isResponseBody;
boolean isVoid;
Pattern urlPattern;
Object controller;
Method handlerMethod;
Param[] methodParameters;
// 1. GET/POST 2. 是否是RestDispatcher 3. Controller Bean 4. Dispatcher 5. URL匹配串
public Dispatcher(String httpMethod, boolean isRest, Object controller, Method method, String urlPattern) throws ServletException {
this.isRest = isRest;
this.isResponseBody = method.getAnnotation(ResponseBody.class) != null;
this.isVoid = method.getReturnType() == void.class;
// 对URL串进行编译 /user/{id}
this.urlPattern = PathUtils.compile(urlPattern);
this.controller = controller;
this.handlerMethod = method;
Parameter[] params = method.getParameters();
Annotation[][] paramsAnnos = method.getParameterAnnotations();
this.methodParameters = new Param[params.length];
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
this.methodParameters[i] = new Param(httpMethod, method, params[i], paramsAnnos[i]);
}
}
}
参数类型如下,具体的见注释:
class Param {
String name;
ParamType paramType;
Class<?> classType;
String defaultValue;
// 1.GET/POST 2. Dispatcher 3. Parameter 4. 注解数组
public Param(String httpMethod, Method method, Parameter parameter, Annotation[] annotations) throws ServletException {
PathVariable pv = ClassUtils.getAnnotation(annotations, PathVariable.class);
RequestParam rp = ClassUtils.getAnnotation(annotations, RequestParam.class);
RequestBody rb = ClassUtils.getAnnotation(annotations, RequestBody.class);
// 一个参数只能有一个注解
int total = (pv == null ? 0 : 1) + (rp == null ? 0 : 1) + (rb == null ? 0 : 1);
if (total > 1) {
throw new ServletException();
}
// 赋值参数类型
this.classType = parameter.getType();
// 赋值注入类型
if (pv != null) {
this.name = pv.value();
this.paramType = ParamType.PATH_VARIABLE;
} else if (rp != null) {
this.name = rp.value();
this.defaultValue = rp.defaultValue();
this.paramType = ParamType.REQUEST_PARAM;
} else if (rb != null) {
this.paramType = ParamType.REQUEST_BODY;
} else {
// 到这一步就是判断是否是Servlet域对象
this.paramType = ParamType.SERVLET_VARIABLE;
if (this.classType != HttpServletRequest.class && this.classType != HttpServletResponse.class && this.classType != HttpSession.class
&& this.classType != ServletContext.class) {
// 如果都不是就报错
throw new ServerErrorException();
}
}
}
}
DispatchServlet#init
我们知道Servlet中有一个init生命周期方法,我们可以在init中来收集所有控制器:
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
ViewResolver viewResolver;
String resourcePath;
String faviconPath;
// 所有Get请求的Dispatcher列表
List<Dispatcher> getDispatchers = new ArrayList<>();
// 所有Post请求的Dispatcher列表
List<Dispatcher> postDispatchers = new ArrayList<>();
public void init() throws ServletException {
for (var def : ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) this.applicationContext).findBeanDefinitions(Object.class)) {
Class<?> beanClass = def.getBeanClass();
Object bean = def.getRequiredInstance();
// 从IOC中拿出所有带有@Controller或@RestController的Bean,执行addController方法
Controller controller = beanClass.getAnnotation(Controller.class);
RestController restController = beanClass.getAnnotation(RestController.class);
if (controller != null && restController != null) {
throw new ServletException();
}
if (controller != null) {
addController(false, def.getName(), bean);
}
if (restController != null) {
addController(true, def.getName(), bean);
}
}
}
}
addController底层调用addMethods,如下:
void addMethods(boolean isRest, String name, Object instance, Class<?> type) throws ServletException {
for (Method m : type.getDeclaredMethods()) {
GetMapping get = m.getAnnotation(GetMapping.class);
if (get != null) {
checkMethod(m);
this.getDispatchers.add(new Dispatcher("GET", isRest, instance, m, get.value()));
}
PostMapping post = m.getAnnotation(PostMapping.class);
if (post != null) {
checkMethod(m);
this.postDispatchers.add(new Dispatcher("POST", isRest, instance, m, post.value()));
}
}
Class<?> superClass = type.getSuperclass();
if (superClass != null) {
addMethods(isRest, name, instance, superClass);
}
}
处理请求
处理请求是Tomcat调用Servlet的service方法,但是HttpServlet对其进行了重写,我们可以在此基础上稍稍改动一下:
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String url = req.getRequestURI();
if (url.equals(this.faviconPath) || url.startsWith(this.resourcePath)) {
doResource(url, req, resp);
} else {
doService(req, resp, this.getDispatchers);
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doService(req, resp, this.postDispatchers);
}
除了Get请求中获取静态资源的方法,最终都会走doService方法,静态资源方法很简单,如下:
void doResource(String url, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
ServletContext ctx = req.getServletContext();
try (InputStream input = ctx.getResourceAsStream(url)) {
if (input == null) {
resp.sendError(404, "Not Found");
} else {
// guess content type:
String file = url;
int n = url.lastIndexOf('/');
if (n >= 0) {
file = url.substring(n + 1);
}
String mime = ctx.getMimeType(file);
if (mime == null) {
mime = "application/octet-stream";
}
resp.setContentType(mime);
ServletOutputStream output = resp.getOutputStream();
input.transferTo(output);
output.flush();
}
}
}
我们来看动态请求的核心代码:
void doService(String url, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, List<Dispatcher> dispatchers) throws Exception {
for (Dispatcher dispatcher : dispatchers) {
// 循环传入的Dispatcher,看一下谁能够处理,当被处理后,我们通过returnObject拿到返回值。
Result result = dispatcher.process(url, req, resp);
if (result.processed()) {
Object r = result.returnObject();
// 处理RestController
if (dispatcher.isRest) {
// 设置setContentType为json,注意每次操作返回值时,都要判断一下response是否已经提交(关闭)。
if (!resp.isCommitted()) {
resp.setContentType("application/json");
}
if (dispatcher.isResponseBody) {
if (r instanceof String s) {
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
pw.write(s);
pw.flush();
} else if (r instanceof byte[] data) {
// send as response body:
ServletOutputStream output = resp.getOutputStream();
output.write(data);
output.flush();
} else {
// error:
throw new ServletException();
}
} else if (!dispatcher.isVoid) {
// 是Rest请求但是返回值不是@ResponseBody那么我们需要将其序列化
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
JsonUtils.writeJson(pw, r);
pw.flush();
}
} else {
// 处理Controller
if (!resp.isCommitted()) {
// 设置为Html类型
resp.setContentType("text/html");
}
if (r instanceof String s) {
if (dispatcher.isResponseBody) {
// send as response body:
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
pw.write(s);
pw.flush();
} else if (s.startsWith("redirect:")) {
// send redirect:
resp.sendRedirect(s.substring(9));
} else {
// error:
throw new ServletException();
}
} else if (r instanceof byte[] data) {
if (dispatcher.isResponseBody) {
// send as response body:
ServletOutputStream output = resp.getOutputStream();
output.write(data);
output.flush();
} else {
// error:
throw new ServletException();
}
} else if (r instanceof ModelAndView mv) {
String view = mv.getViewName();
if (view.startsWith("redirect:")) {
// send redirect:
resp.sendRedirect(view.substring(9));
} else {
this.viewResolver.render(view, mv.getModel(), req, resp);
}
} else if (!dispatcher.isVoid && r != null) {
// error:
throw new ServletException();
}
}
return;
}
}
// not found:
resp.sendError(404, "Not Found");
}
在整个HTTP处理流程中,入口是DispatcherServlet的service()方法,整个流程如下:
- Servlet容器调用
DispatcherServlet的service()方法处理HTTP请求; service()根据GET或POST调用doGet()或doPost()方法;- 根据URL依次匹配
Dispatcher,匹配后调用process()方法,获得返回值; - 根据返回值写入响应:
- void或null返回值无需写入响应;
- String或byte[]返回值直接写入响应(或重定向);
- REST类型写入JSON序列化结果;
- ModelAndView类型调用ViewResolver写入渲染结果。
- 未匹配到判断是否静态资源:
- 符合静态目录(默认
/static/)则读取文件,写入文件内容; - 网站图标(默认
/favicon.ico)则读取.ico文件,写入文件内容;
- 符合静态目录(默认
- 其他情况返回404。
Filter
最后我们来实现Filter,我们这里只提供了REQUEST类型的Filter,如下,我们在Container创建时,将IOC中符合条件的Bean注册到ServletContext中去:
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
// ...
// register filters:
WebUtils.registerFilters(servletContext);
// register DispatcherServlet:
WebUtils.registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext, propertyResolver);
servletContext.setAttribute("applicationContext", applicationContext);
}
注册的具体逻辑如下,我们遍历IOC拿到类型为FilterRegistrationBean的所有Bean,将其绑定。
public static void registerFilters(ServletContext servletContext) {
var applicationContext = ApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredApplicationContext();
for (var filterRegBean : applicationContext.getBeans(FilterRegistrationBean.class)) {
List<String> urlPatterns = filterRegBean.getUrlPatterns();
if (urlPatterns == null || urlPatterns.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No url patterns for {}" + filterRegBean.getClass().getName());
}
var filter = Objects.requireNonNull(filterRegBean.getFilter(), "FilterRegistrationBean.getFilter() must not return null.");
var filterReg = servletContext.addFilter(filterRegBean.getName(), filter);
filterReg.addMappingForUrlPatterns(EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST), true, urlPatterns.toArray(String[]::new));
}
}
FilterRegistrationBean的定义如下:
public abstract class FilterRegistrationBean {
public abstract List<String> getUrlPatterns();
/**
* Get name by class name. Example:
*
* ApiFilterRegistrationBean -> apiFilter
*
* ApiFilterRegistration -> apiFilter
*
* ApiFilterReg -> apiFilterReg
*/
public String getName() {
String name = getClass().getSimpleName();
name = Character.toLowerCase(name.charAt(0)) + name.substring(1);
if (name.endsWith("FilterRegistrationBean") && name.length() > "FilterRegistrationBean".length()) {
return name.substring(0, name.length() - "FilterRegistrationBean".length());
}
if (name.endsWith("FilterRegistration") && name.length() > "FilterRegistration".length()) {
return name.substring(0, name.length() - "FilterRegistration".length());
}
return name;
};
public abstract Filter getFilter();
}
我们只需要实现这个类,将其注入到IOC即可,具体的用例如下:
@Order(200)
@Component
public class ApiFilterRegistrationBean extends FilterRegistrationBean {
@Override
public List<String> getUrlPatterns() {
return List.of("/api/*");
}
@Override
public Filter getFilter() {
return new ApiFilter();
}
}
class ApiFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
if (!resp.isCommitted()) {
resp.reset();
resp.setStatus(400);
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
JsonUtils.writeJson(pw, Map.of("error", true, "type", e.getClass().getSimpleName(), "message", e.getMessage() == null ? "" : e.getMessage()));
pw.flush();
}
}
}
}
End
一些具体的ModeView不再叙述,使用的是FreeMarker引擎。
最后创建配置类WebMvcConfiguration:
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfiguration {
private static ServletContext servletContext = null;
/**
* Set by web listener.
*/
static void setServletContext(ServletContext ctx) {
servletContext = ctx;
}
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
ViewResolver viewResolver(
@Autowired ServletContext servletContext,
@Value("${summer.web.freemarker.template-path:/WEB-INF/templates}") String templatePath, //
@Value("${summer.web.freemarker.template-encoding:UTF-8}") String templateEncoding) {
return new FreeMarkerViewResolver(servletContext, templatePath, templateEncoding);
}
@Bean
ServletContext servletContext() {
return Objects.requireNonNull(servletContext, "ServletContext is not set.");
}
}